beer_mkts <- read_csv("https://bcdanl.github.io/data/beer_markets.csv")Let’s analyze the beer_mkts data:
rmarkdown::paged_table(beer_mkts) Variable Description for beer_mkts data.frame
The following describes the variables in the beer_mkts data.frame.
hh: Household identifier_purchase_desc: Description of the purchasequantity: The quantity of beer purchasedbrand: The brand of beerdollar_spent: The amount spentbeer_floz: Fluid ounces of beerprice_per_floz: Price per fluid ouncecontainer: Type of containerpromo: Whether the purchase was on promotionmarket: The market where the purchase was made- Demographics:
age,employmentstatus,degree, class of worker (cow),race, and household information likemicrowave,dishwasher,tvcable,singlefamilyhome, andnpeople(number of people in the household)
Purchase Patterns
We’ll explore the purchase patterns for beer purchases in the dataset. This will include finding the most popular brands and spending habits across different markets. Here are some specific analyses we can perform:
Find top markets in terms of total quantity for each brand.
Compare the proportion of loyal customers.
I’ll begin with these analyses and create visualizations to help us understand the data better. I will start by finding the top 5 markets in terms of the total beer_floz.
top_5 <- beer_mkts %>%
group_by(market) %>%
summarize(beer_floz_tot = sum(beer_floz, na.rm = T)) %>%
arrange(-beer_floz_tot) %>%
slice(1:5)Let’s visualize the top 5 markets in terms of the total beer_floz.
ggplot(top_5, aes(x = market, y = beer_floz_tot)) +
geom_bar(stat = "identity", fill = "skyblue") +
labs(title = "Top 5 Beer Markets",
x = "Market",
y = "Total Beer (floz)")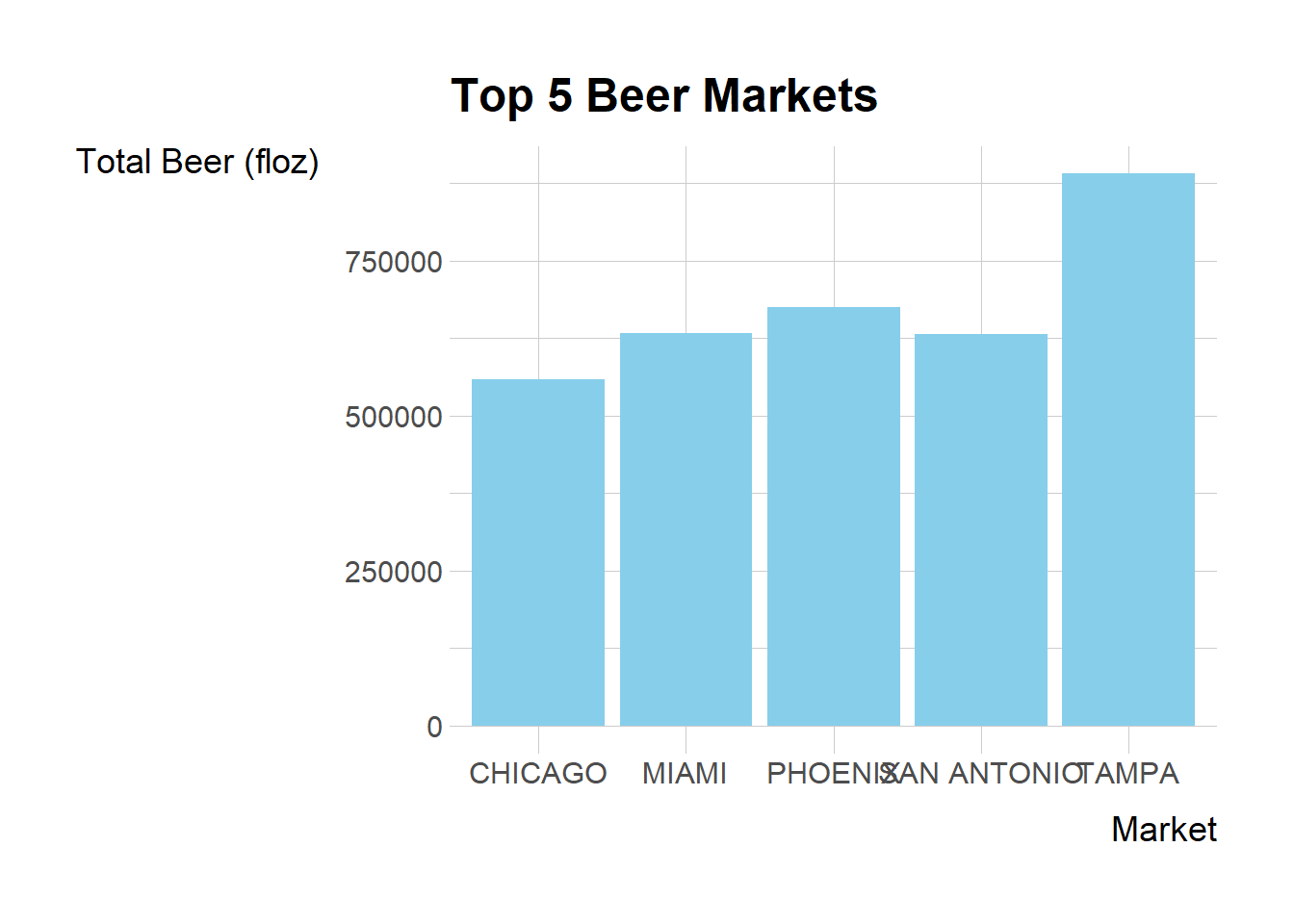
Next, we can look at the top 5 markets in terms of the total beer_floz of a specific brand. For example, BUD LIGHT:
top_5_bud <- beer_mkts %>%
filter(brand == "BUD LIGHT") %>%
group_by(market) %>%
summarize(beer_floz_tot = sum(beer_floz, na.rm = T)) %>%
arrange(-beer_floz_tot) %>%
slice(1:5)Just like the top 5 beer markets, let’s visualize the top 5 markets for BUD LIGHT.
ggplot(top_5_bud, aes(x = market, y = beer_floz_tot)) +
geom_bar(stat = "identity") +
labs(title = "Top 5 Beer Markets - Bud Light",
x = "Market",
y = "Total Beer (floz)")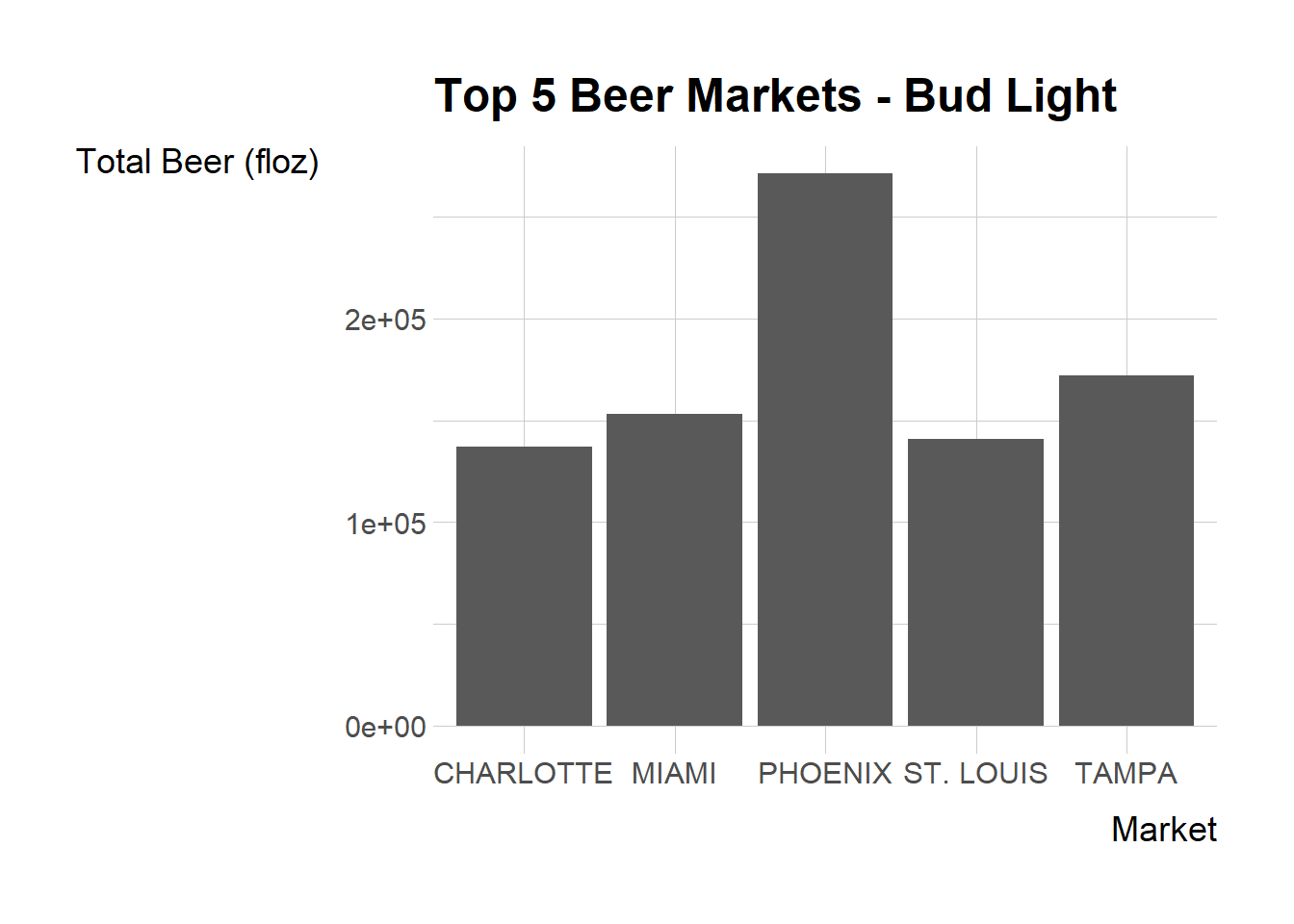
I will do the same for BUSCH LIGHT, COORS LIGHT, MILLER LITE, and NATURAL LIGHT.
top_5_busch <- beer_mkts %>%
filter(brand == "BUSCH LIGHT") %>%
group_by(market) %>%
summarize(beer_floz_tot = sum(beer_floz, na.rm = T)) %>%
arrange(-beer_floz_tot) %>%
slice(1:5)
top_5_coors <- beer_mkts %>%
filter(brand == "COORS LIGHT") %>%
group_by(market) %>%
summarize(beer_floz_tot = sum(beer_floz, na.rm = T)) %>%
arrange(-beer_floz_tot) %>%
slice(1:5)
top_5_miller <- beer_mkts %>%
filter(brand == "MILLER LITE") %>%
group_by(market) %>%
summarize(beer_floz_tot = sum(beer_floz, na.rm = T)) %>%
arrange(-beer_floz_tot) %>%
slice(1:5)
top_5_natural <- beer_mkts %>%
filter(brand == "NATURAL LIGHT") %>%
group_by(market) %>%
summarize(beer_floz_tot = sum(beer_floz, na.rm = T)) %>%
arrange(-beer_floz_tot) %>%
slice(1:5)Let’s also look at a visualization for BUSCH LIGHT:
ggplot(top_5_busch, aes(x = market, y = beer_floz_tot)) +
geom_bar(stat = "identity") +
labs(title = "Top 5 Beer Markets - Busch Light",
x = "Market",
y = "Total Beer (floz)")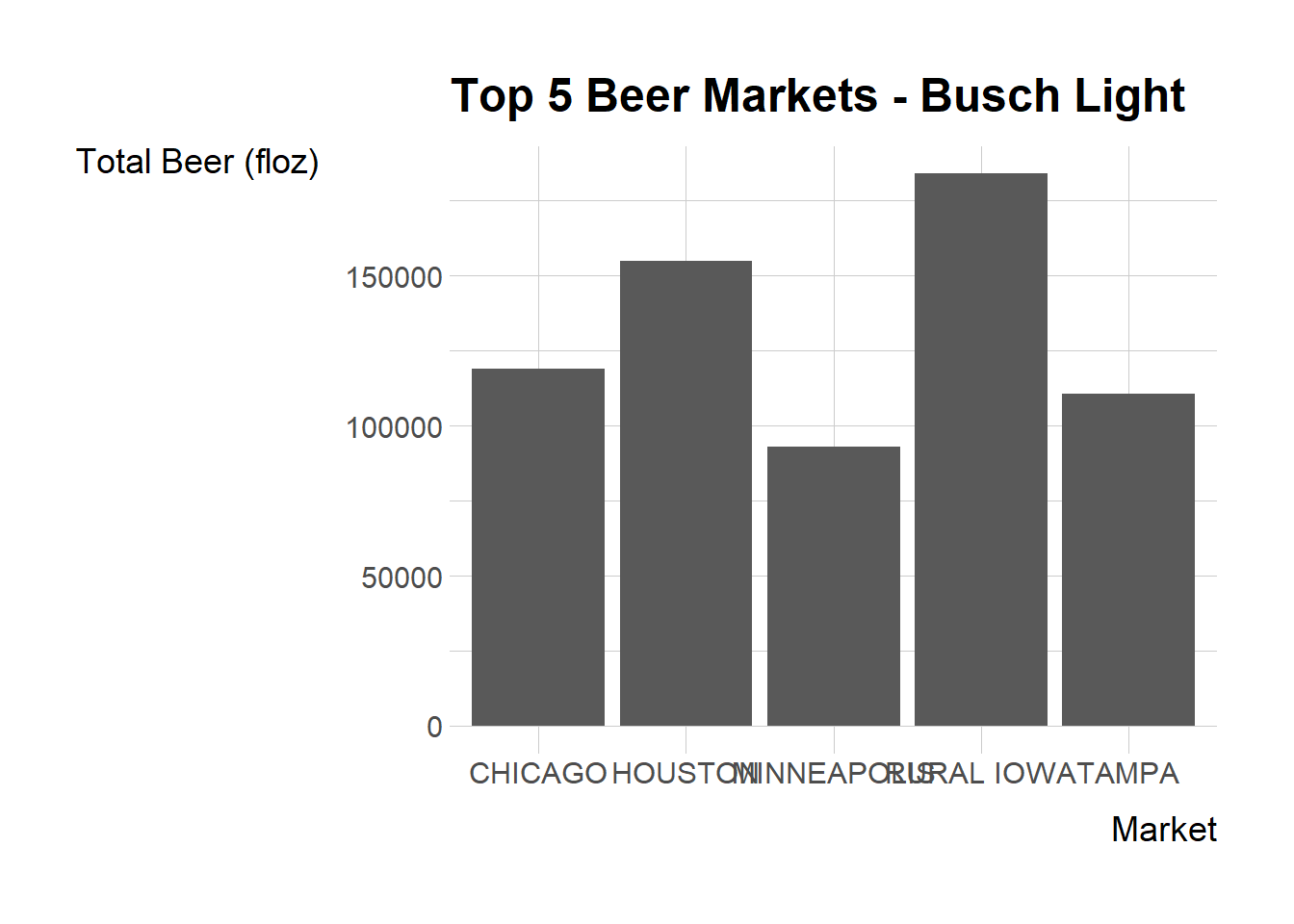
Next, we will evaluate proportions of loyal customers for each brand. For example, for households that purchased BUD LIGHT at least once, I will find the fraction of households that purchased only BUD LIGHT. I will find the proportion of loyal customers for all 5 brands.
loyal_customers <- beer_mkts %>%
mutate(bud = ifelse(brand=="BUD LIGHT", 1, 0), # 1 if brand=="BUD LIGHT"; 0 otherwise
busch = ifelse(brand=="BUSCH LIGHT", 1, 0),
coors = ifelse(brand=="COORS LIGHT", 1, 0),
miller = ifelse(brand=="MILLER LITE", 1, 0),
natural = ifelse(brand=="NATURAL LIGHT", 1, 0),
.after = hh) %>%
select(hh:natural) %>% # select the variables we need
group_by(hh) %>%
summarise(n_transactions = n(), # number of beer transactions for each hh
n_bud = sum(bud), # number of BUD LIGHT transactions for each hh
n_busch = sum(busch),
n_coors = sum(coors),
n_miller = sum(miller),
n_natural = sum(natural)
) %>%
summarise(loyal_bud = sum(n_transactions == n_bud) / sum(n_bud > 0),
# sum(n_transactions == n_bud) : the number of households that purchased BUD LIGHT only
# sum(n_bud > 0) : the number of households that purchased BUD LIGHT at least once.
loyal_busch = sum(n_transactions == n_busch) / sum(n_busch > 0),
loyal_coors = sum(n_transactions == n_coors) / sum(n_coors > 0),
loyal_miller = sum(n_transactions == n_miller) / sum(n_miller > 0),
loyal_natural = sum(n_transactions == n_natural) / sum(n_natural > 0)
)